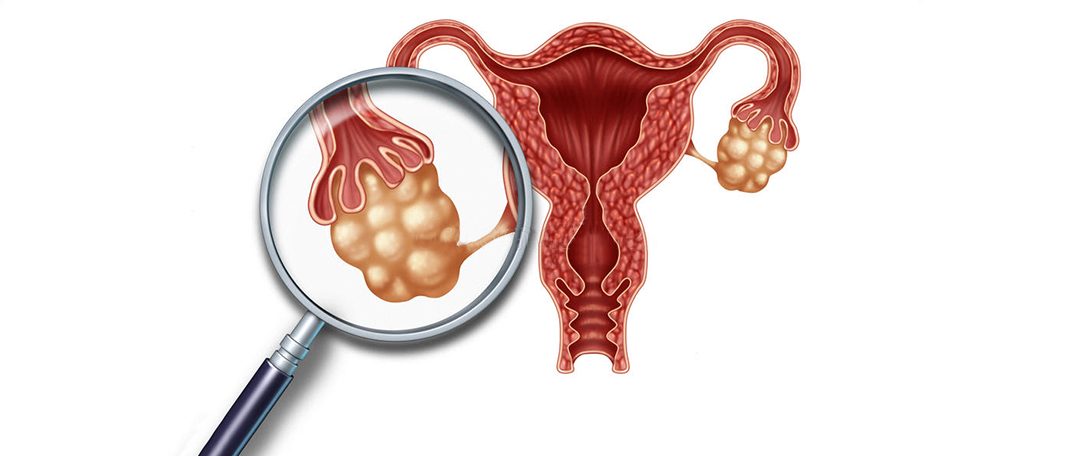
The ovaries are a part of the female reproductive system. Eggs/ovum are tiny organs about the size of an almond, produced by the ovaries. Estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, and androgens are some hormones produced by the ovaries. The two ovaries are three to five centimeters each in a female body. They play a significant role in a woman’s menstrual cycle and pregnancy, by producing eggs for reproduction. The eggs travel through the fallopian tube and reach out to the uterus, where the baby grows.
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer occurs when there is mutilation in the DNA of the cells. When the cells grow in excess, they act abnormally and create tumors. These cancer cells invade and destroy the healthy cells and spread to the other body parts, eventually weakening the body. The ovarian cancer cell will not necessarily develop in the ovaries but can also develop in the fallopian tube and spread to the ovaries.
Symptoms of ovarian cancer
The symptoms usually do not show up in the beginning. Listed below are the symptoms of ovarian cancer.
- Fatigue
- Bloating
- Back pain
- Pelvic pain
- Abdominal pain
- Feeling full even after eating less
- Painful sex
- Irregular periods or heavy bleeding than normal
- Weight loss
- Vaginal bleeding
Which vaccine protects against ovarian cancer?
The HPV-Gardasil 9 vaccine is usually mistaken to be an ovarian cancer vaccine. There is no vaccine against ovarian cancer. The HPV-Gardasil 9 vaccine prevents cervical, pelvic, and vaginal cancer ‘if’ taken before the invasion of a cancer cell.
Overview of HPV vaccine
HPV stands for Human “Papillomavirus.” The HPV virus can spread through sexual activity, and a majority of people will contract it at some time in their life. Fortunately, most people’s bodies are immune to the virus and can fight it without medical intervention. The cancers: cervical, vaginal, vulval, anal, penis, head, and neck cancers are all brought on by specific high-risk forms of HPV. Some types of the HPV virus can cause genital and skin warts, verrucas, and vocal cord warts. Two doses of the HPV vaccine are administered, with a six-month interval between each.
Why can’t adults get the HPV vaccine?
Between the ages of 9 and 26 is the recommended range for HPV vaccination. The primary goal of the HPV vaccine is to prevent the virus before individuals become sexually active since it spreads through sex and physical contact. Before getting the shot, patients over 26 years should speak with their doctor. The HPV vaccine has less of an impact on older people because they may have already been exposed to HPV.
How to Prevent Ovarian Cancer
The chance of getting ovarian cancer can increase in those with genital mutations and in those with a family history of cancer. A balanced lifestyle and healthy eating habits can lower the risk. Consuming foods like carrots, beans, almonds, and leafy greens that are high in vitamin A and vitamin D is a good idea. Avoiding tobacco and drinking alcohol in moderation is the finest thing you can do for your health and your life.