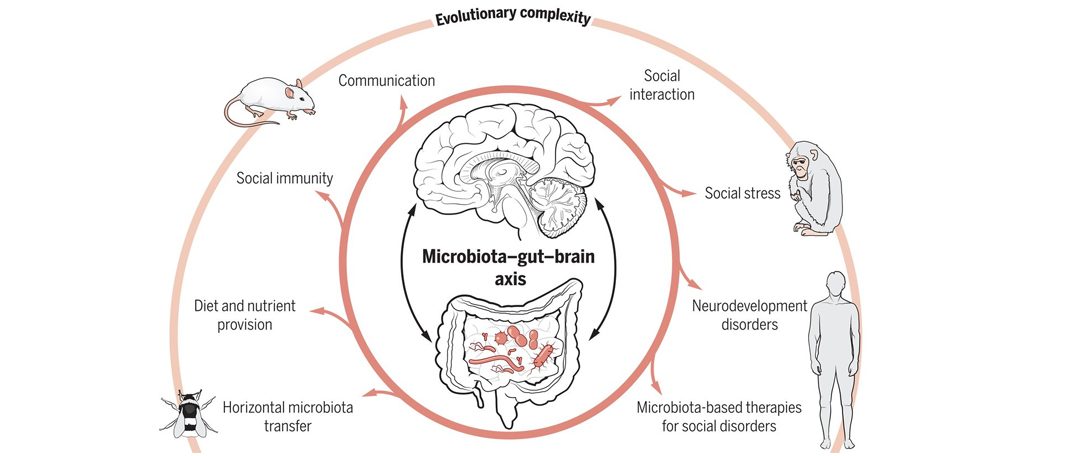
The Gut-Brain Axis is the biochemical signaling between the Central Nervous System(CNS) and the Gastrointestinal Tract(GI). The Gut-Brain Axis is also regulated through the neural, endocrine, immune, and metabolic pathways, and especially including the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.
How Gut and Brain Are Connected?
To put in simple terms the communication between the gut and brain is known as the gut-brain axis. The gut and the brain are connected by both physical and biochemical ways.
The Vagus Nerve – Neuron cells are found in your brain and central nervous system. There are nearly 100 billion neurons in the human brain at the same time there are nearly 500 million neurons in the gut which are connected to your central nervous system. The vagus nerve connects both your brain and the gut which sends signals in both directions. The vagus nerve is the largest nerve in the human body which also plays a vital role in stress disorder.
Neurotransmitters – The chemical which connects both the gut and the brain are called neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitters produced in the body helps to control the feelings and emotions. The neurotransmitters were also produced by the gut cells. Gamma-aminobutyric acid( GABA) is a type of neurotransmitter produced by the microbes which help control the feeling of anxiety and fear.
What Is Gut Microbiota?
Gut microbiota is the microorganism( bacteria, fungi, and archaea) that live inside the digestive tract of the human and animal body. Gut Microbiota also called Gut flora plays an important role in the human body like digesting food and increasing our immune system. The Gut microbiota is located in the gut of the human body.
Impaired Microbiota or Dysbiosis is a microbial imbalance in the human body that can lead to both internal and external intestinal diseases like inflammatory bowel disease, cancer, metabolic syndrome, obesity, diabetes, and atopy. Recent researches have proved that dysbiosis can also lead to a neurological disorder like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, autism, multiple sclerosis.
How Gut Microbiota Affects the Brain?
The Gut has trillions of microbes that produce chemicals to affect the function of your brain.
Short Chain Fatty Acids(SCFA) like butyrate, propionate, and acetate were produced by the microbes. The SCFA affects the brain function by reducing its appetite and it also acts as a barrier between the blood and the brain known as the Blood-brain barrier. Bile acids produced in the kidney also affect the brain.
How the Gut-Brain Axis Cures Neurological Disorder?
The Gut-brain axis has a bidirectional communication system between the central nervous system(CNS) and the enteric nervous system(ENS) of the body, Which links the emotional and cognitive centers of the brain with the peripheral intestinal function. When the brain is troubled it sends a signal to the gut and when the stomach is troubled it sends a signal to the brain, as the central nervous system and the intestinal tract are connected together.
To improve the health of your brain, it’s necessary to alter the type of bacteria in your gut. Probiotics and prebiotics are the live bacteria in the gut that affects the brain system and reduces stress, depression, and anxiety disorder. The prebiotic called galactooligosaccharides reduce the stress hormone from the body called cortisol.
Food That Helps the Gut-Brain Axis
- Omega 3 fats – Omega 3 can reduce the risk of brain disorder and increase the formation of good bacteria in the gut. These fats are found in oily fish.
- Fermented foods – Fermented foods can change the activity of the brain. The fermented food which contains lactic acid bacteria is yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and cheese.
- High fiber foods – The high fiber foods include whole grains, nuts, and seeds, fruits, and veggies that contain prebiotic fibers that induce good gut bacteria. It reduced the stress hormones from your body.
- Polyphenol-rich foods – polyphenols increase the healthy gut bacteria and improve cognition. The polyphenol-rich food includes Cocoa, green tea, and olive oil which are assumed as plant chemicals.
- Tryptophan-rich foods – Tryptophan-rich foods include turkey, eggs, and cheese, it also acts as an amino acid that is converted into neurotransmitter serotonin.
Keeping our gut clean will protect us against various disorders. There are many foods that are a major threat to our gut and nervous system. At the same time eliminating some foods like grains also creates an impairment to our gut. So it is important to take care of our gut otherwise it may lead to stress, depression, and neurological disorders which are becoming a great threat in this century.