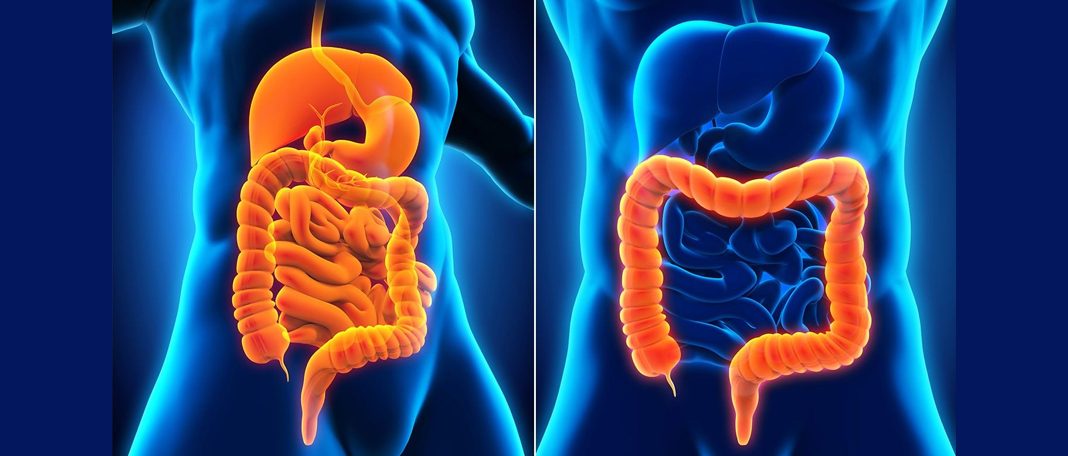
Crohn’s Disease vs Ulcerative Colitis, why has Crohn’s affected half a million Americans? Why is ulcerative colitis spreading in North America and Europe? Here is everything you should know.
What Is Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is an inflammatory disease that affects the intestine. Though it is not life-threatening in nature, it can compromise an individual’s health severely. There are five types:
- Ileocolitis – Ileum and colon inflate.
- Ileitis– Inflated ileum coupled with irritation.
- Gastroduodenal– Inflammation in the esophagus, stomach, and/or duodenum.
- Jejunoileitis– The upper half of the small intestine inflates.
- Crohn’s (Granulomatous) Colitis– Inflammation in the colon.
What Causes Crohn’s Disease
The Crohn’s disease pain does not manifest until the disease has progressed aggressively. Hereditary and a weak immune system are assumed to cause the disease while diet and stress can further aggravate the conditions.
Crohn’s Disease Symptoms
The common signs of Crohn’s Disease are nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, appetite loss, weight loss, fullness, and anal fissures. There is no definite treatment for Crohn’s Disease. Doctors often prescribe medication and lifestyle changes that could prevent the disease from aggravating and reduce the ill effects of symptoms.
What Is Ulcerative Colitis
There are five types of colitis:
- Ulcerative colitis– Inflammation in the colon and rectum.
- Pseudomembranous colitis– Inflammation caused by antibiotics.
- Ischemic colitis– Inflammation caused due to lack of blood flow.
- Microscopic colitis– Inflammation is visible only under a microscope.
- Allergic colitis in infants– They can exhibit eczema, nasal congestion, or any other allergic reaction.
Ulcerative Colitis is a common IBD (inflammatory bowel disease) that has been affecting several North Americans and Europeans. The disease causes inflammation in the colon and the rectum. UC can be further divided into five types:
- Acute severe UC – The entire colon is affected
- Left-sided colitis– The descending colon and rectum are affected
- Pancolitis– The entire colon develops ulcers.
- Proctosigmoiditis– Only the rectum and lower colon are affected.
- Ulcerative proctitis– Only the rectum is affected.
What Causes Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative Colitis is considered to be a chronic auto-immune disease. The immune system protects against the intrusion of pathogens by releasing white blood cells. The abundant white cells cause redness and inflammation. U.C. occurs when the immune system mistakes good bacteria residing in the colon as a pathogen. Ethnic groups have a higher risk of contracting the disease. There is a high risk of acquiring colon or colorectal cancer.
Ulcerative Colitis Symptoms
There is no treatment for Ulcerative Colitis. This is a chronic life-threatening condition. The common symptoms of ulcerative colitis are mild to severe cramping in the abdomen and rectum, loose stools, and eating difficulties. Ulcerative Colitis medications can ease the symptoms and remission.
Crohn’s Disease vs Ulcerative Colitis
Here is a table that will help you differentiate between Crohn’s and colitis disease:
| Difference | Crohn’s Disease | Ulcerative Colitis |
| Condition | Chronic and incurable IBD | Chronic and incurable IBD |
| Treatment | Medication to ease pain and symptoms | Medication and surgery to ease pain and symptoms |
| Area | Mouth to Anus | Colon |
| Spread of Infection | Is Blotched | Is Continuous |
| Occurrence | Layers of infection | Affects the innermost tissue |
| Affects | Americans Majorly | North American’s and Europeans |
Constipation, passing small quantities of stool with or without blood is a common symptom for both Crohn’s and Colitis. Indeterminate colitis exhibit symptoms of both Crohn’s and Colitis disease.