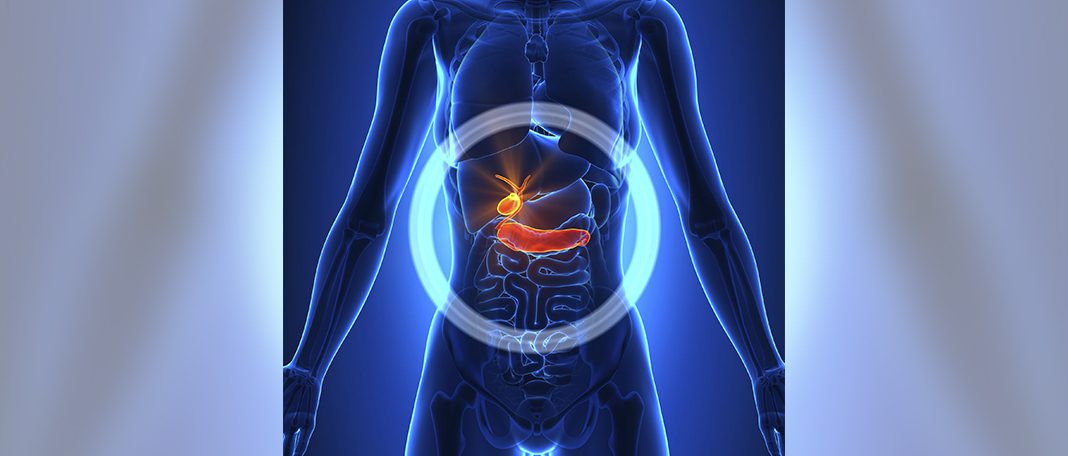
Gallbladder is a small pear shaped four-inch organ that sits just under the liver in the upper abdomen. The function of gallbladder is to store bile, which helps the digestive system to break down fats. When the food enters the small intestine, cholecystokinin ( a hormone) is released, signaling the gallbladder to contract and secrete bile into the small intestine. This process allows the fat-soluble vitamins and nutrients to be easily absorbed into the bloodstream.
In most cases, gallstones block the bile from existing the organ leading to Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder. Nearly 120,000 Americans are treated for acute cholecystokinin every year.
What are the symptoms of Gallbladder?
Pain
Pain is the most common symptom of gallbladder problems. The pain usually occurs in the middle to upper-right side of your abdomen. Pain may vary from mild to severe, it may be constant and steady, stabbing or punching, throbbing and pulsating.
Nausea or vomiting
This is the common symptom of all types of gallbladder problems. But, chronic gallbladder diseases can cause digestive problems such as acid reflux and gas.
Fever or chills
High fever or chills indicates bacterial function in the gallbladder. If you don’t treat infection in the beginning stage, it might get worse and become dangerous. It can also spread to other parts of the body and lead to life threatening diseases.
Chronic diarrhea
During inflammation, the gallbladder may become scarred and stiff which can cause four bowel movements per day. If you’re experiencing more than four bowel movements for at least three months then it’s a sign of chronic gallbladder disease.
Jaundice
Jaundice occurs if gallstone passes out of the gallbladder into the bile duct and blocks the flow of bile. The symptoms of jaundice include yellowing of skin, dark brown urine and whites of the eyes.
Unusual stools or urine
Frequent, unexpected and unusual diarrhea are some other symptoms of Cholecystitis. Light coloured, chalky stools, and dark urine may occur if bile ducts are obstructed.
Diagnosis
Your physician might ask you to take the following test-
Ultrasound– This test shows the condition of the gallbladder by highlighting the gallstones.
Blood test– High white blood cells count can confirm the presence of an infection. It also reveals infection, pancreas and other complications caused by gallstones.
Hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid scan (HIDA scan)– HIDA scan helps to evaluate the signs and symptoms in the gallbladder, bile ducts and liver. A tiny amount of radioactive compound is injected into your bloodstream. It travels through your liver, gallbladder and small intestine. A camera tracks and takes picture of its movement
CT or ultrasound scans– This test takes images of your pancreas, gallbladder and bile ducts. CT or ultrasound scans clearly show the presence of infection and blockage of the gallbladder or bile ducts.