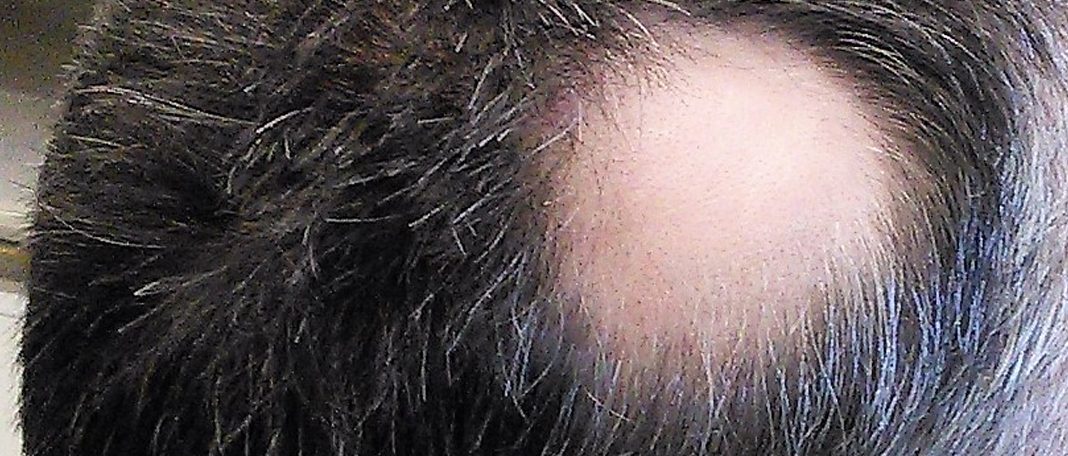
Alopecia, commonly termed as hair loss, is a chronic condition that results in the loss of hair leaving small patches on the head or other parts of the body. Alopecia occurs in both men and women, but is more common in men. This condition is categorized by the extent of hair loss and the varying symptoms.
Some of Alopecia’s common types are:
- Alopecia areata – one or more coin-sized patches are observed after hair loss.
- Alopecia totalis – occurs when a person loses hair across the entire scalp.
- Alopecia universalis – in addition to hair loss in the scalp, the person tends to lose hair on their face and body, especially eyebrows and eyelashes.
- Diffuse alopecia areata – the condition results in sudden thinning of hair all over the scalp.
- Ophiasis alopecia – hair loss is observed along the sides and lower back of the scalp.
What Causes Alopecia?
Alopecia is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the healthy cells, assuming them to be foreign cells. Here, the immune system attacks the body’s hair follicles, making the cells halt the hair production—resulting in hair loss.
Some of the common causes of Alopecia are:
- Family history of conditions like Type-1 Diabetes or Rheumatoid Arthritis.
- Genetics
Although the exact cause of the condition is still not identified.
Alopecia Symptoms:
Though Alopecia is mainly characterized by hair loss, other symptoms contribute to the condition. Some of Alopecia’s symptoms are:
- Hair loss at a fast rate on the scalp and other parts of the body.
- Loss of hair in eyebrows and eyelashes
- Red and brittle fingernails and toenails
Hair loss is the most common symptom of Alopecia and it is important to note the pattern of hair loss to determine the type of Alopecia the person has.
Alopecia Diagnosis:
Alopecia is diagnosed by the pattern and amount of hair loss, and a blood test. A blood test helps in identifying the behavior of the body’s immune system as alopecia occurs when immune cells attack hair follicles.
What is the Best Way to Treat Alopecia?
It is unfortunate that Alopecia does not have a cure yet. There are treatments performed to reduce the extent of hair loss or increase hair growth. People are also warned that the treatments could backfire, as hair loss might get worse for some. Some common treatments followed are:
- Medication for the scalp – medicated lotions and oils can be applied on the scalp to stimulate hair growth. Medications like Minoxidil, Corticosteroid creams, and Anthralin can show good results for people with hair loss.
- Steroid injections – tiny needles with steroids are injected into the affected areas to stimulate hair growth in the patchy areas.
- Oral medication – oral immunosuppressants can be taken to reduce the attack of the immune system on hair follicles, which in turn decreases alopecia symptoms. Cortisone tablets can also be taken for extensive alopecia, but this certain medicine is prone to side effects. It is important to consult your healthcare provider before starting oral or any type of medication.
Alopecia Treatment at Home
Alopecia home remedies are limited but it is always worth giving them a try. Remember to consult a doctor if home remedies do not work. Rubbing certain natural components on the scalp and the affected areas can be a good remedy for alopecia. Some of the common home remedies used for treating alopecia are:
- Onion or garlic juice
- Cool green tea
- Almond oil
- Rosemary oil
- Honey
- Coconut milk